2024-01-31

Throughout human history, the number 3 has always had a unique significance. In Ancient Greek philosophy, the number 3 was considered as the perfect number, the number of harmony, wisdom and understanding.
Recently, the MC-80 Digital Morphology Analyzer underwent rigorous evaluation by 3 top university hospitals worldwide, quickly earning global recognition. The International Journal of Laboratory Hematology recently published three professional evaluation reports on the WBC differential performance of MC-80, providing insights from different perspectives.
Rome, Italy
\r\n“Advances in technology mean that moving from microscopes to digital alternatives can now be achieved without sacrificing image quality.” Professor Gina Zini shares her views on the main benefits of digital development, including better quality screening, time savings for busy morphologists, better clinical collaboration, and improved training in the interview.[1] Prof. Zini is very concerned about the application of this technology in the most challenging hematology departments. After conducting a systematic and rigorous evaluation of the MC-80, she called this work "artificial intelligence and blood film"! [2]
\r\n"}}" id="text-bd95ec5683" class="8f00b2 cmp-text">Rome, Italy
“Advances in technology mean that moving from microscopes to digital alternatives can now be achieved without sacrificing image quality.” Professor Gina Zini shares her views on the main benefits of digital development, including better quality screening, time savings for busy morphologists, better clinical collaboration, and improved training in the interview.[1] Prof. Zini is very concerned about the application of this technology in the most challenging hematology departments. After conducting a systematic and rigorous evaluation of the MC-80, she called this work "artificial intelligence and blood film"! [2]

It’s a two-university study. A vast proportion of samples from hematology patients with blood disorders and a few with viral infections (591 patients in total) were selected to include most types of cells that do not normally circulate in the peripheral blood.

The results confirm the excellent internal consistency of the MC-80 differential count, even in the presence of abnormal cells.
\r\n"}}" id="text-22e6ff6361" class="8f00b2 cmp-text">The results confirm the excellent internal consistency of the MC-80 differential count, even in the presence of abnormal cells.
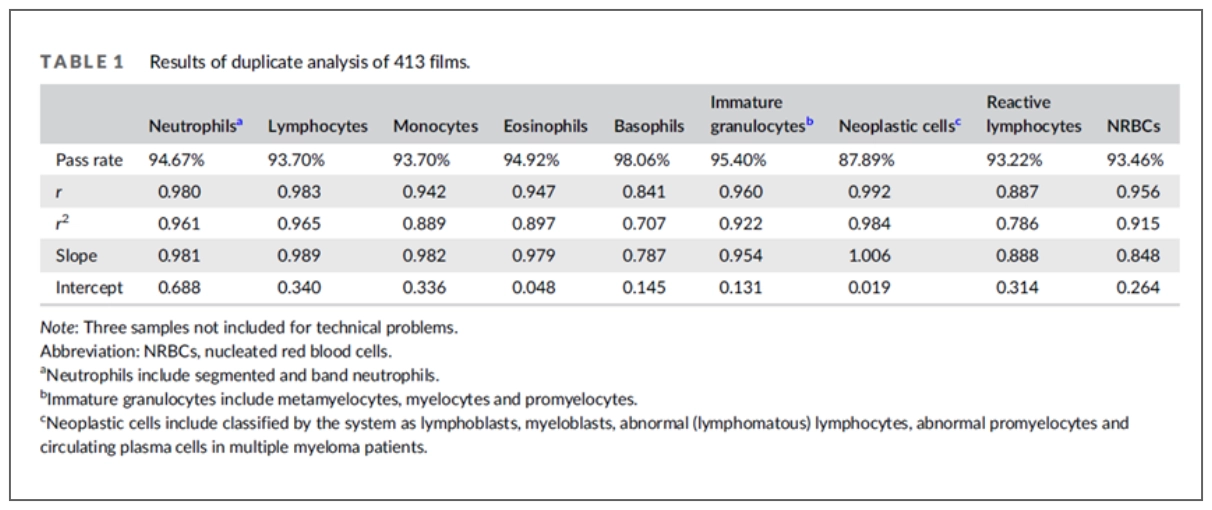
The correlation coefficients (r) between MC-80 post-classification results and manual differential (reference) for the five types of normal leukocytes and the four primary populations of abnormal cells are high for all types of cells except for reactive lymphocytes.
\r\n"}}" id="text-a2e58a20dd" class="8f00b2 cmp-text">The correlation coefficients (r) between MC-80 post-classification results and manual differential (reference) for the five types of normal leukocytes and the four primary populations of abnormal cells are high for all types of cells except for reactive lymphocytes.
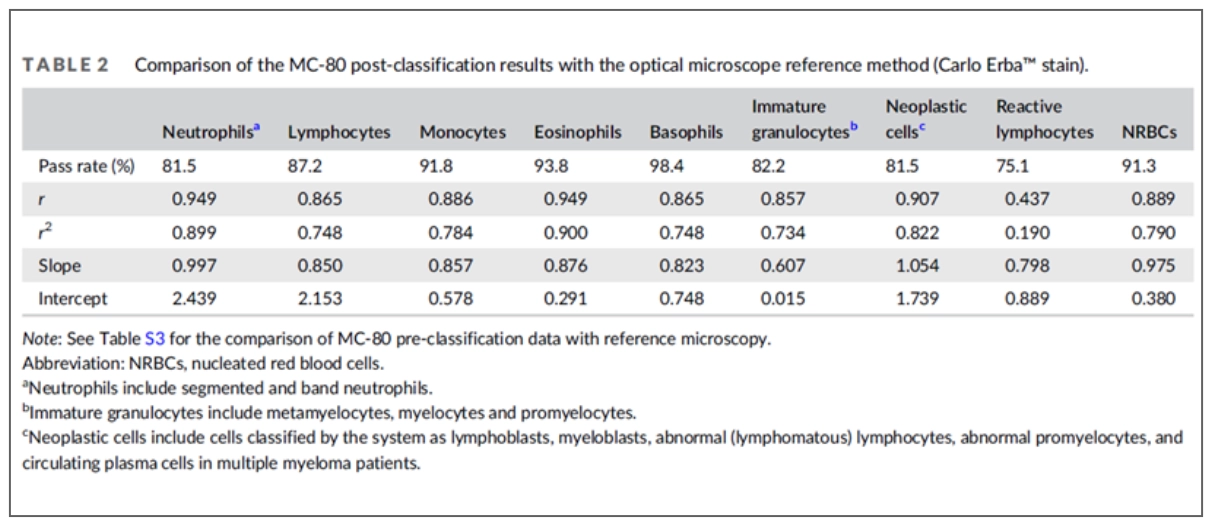
The results between pre-classification and the post-classification MC-80 results are compared too. It’s reported, differences between the major normal leukocyte classes were minimal, while the most relevant adjustments due to the operators' revision (post-classification) were observed for basophils and reactive lymphocytes.

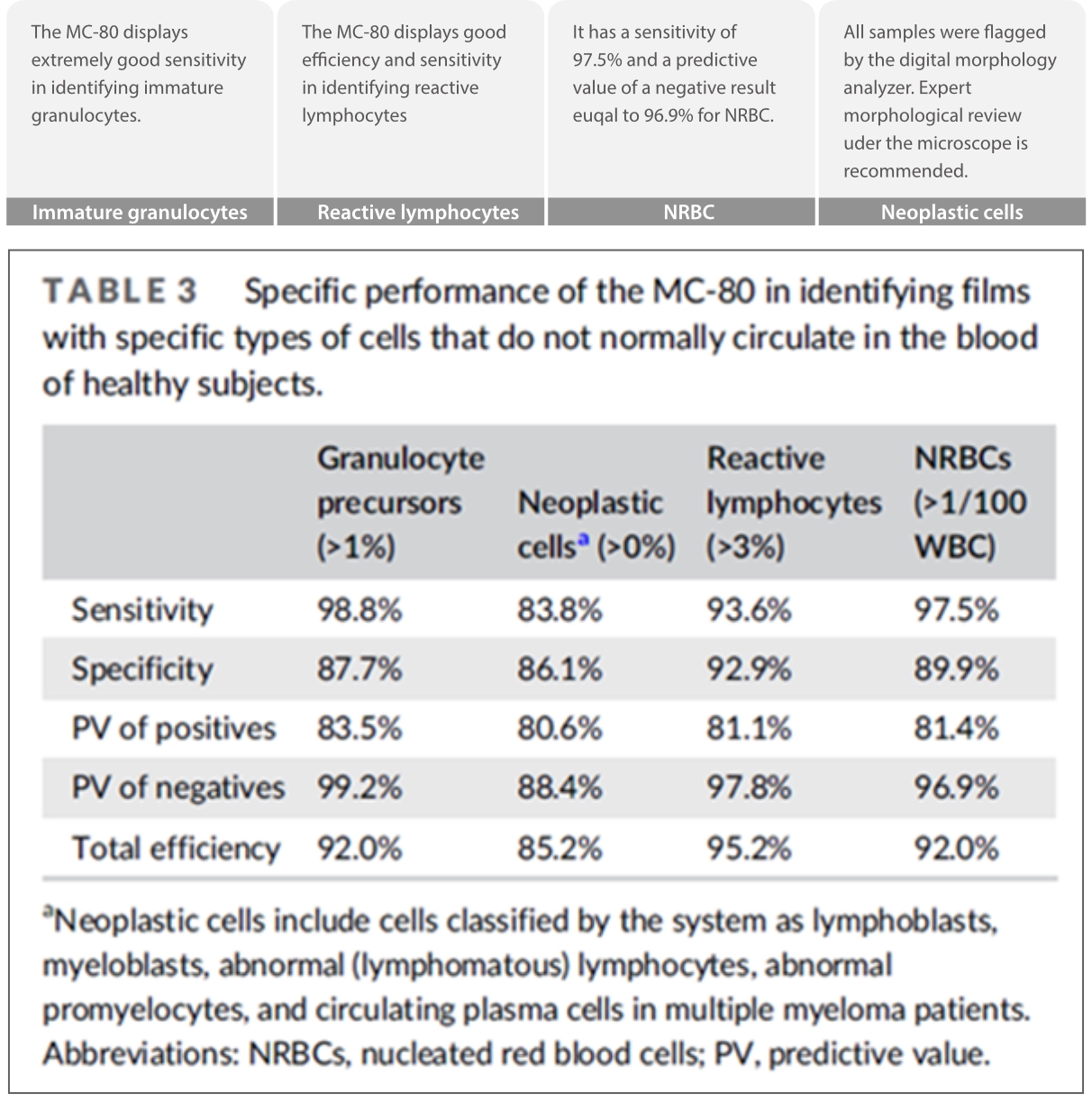
“Our study highlights the outstanding diagnostic performance of this artificial intelligence–based blood film analyzer for hematology patients with circulating abnormal cells. We appreciated the morphological harmonization of cells observed on the screen and those seen in the microscope.”
\r\n
“Our study highlights the outstanding diagnostic performance of this artificial intelligence–based blood film analyzer for hematology patients with circulating abnormal cells. We appreciated the morphological harmonization of cells observed on the screen and those seen in the microscope.”
Barcelona, Spain
\r\nBarcelona, Spain

A total of 445 samples were used, and WBC pre-classification values with the MC-80 and DM9600 were compared with the manual reference (microscope), Mindray BC-6800Plus differentials (only normal samples), and confirmed or reclassified images (post-classification). [3]
The pre-classification and post-classification of WBC using the MC-80 and DM9600 in normal samples were compared with the manual reference method using the microscope and with the differential leukocyte count (DLC) obtained on the BC-6800Plus.
\r\n
The pre-classification and post-classification of WBC using the MC-80 and DM9600 in normal samples were compared with the manual reference method using the microscope and with the differential leukocyte count (DLC) obtained on the BC-6800Plus.
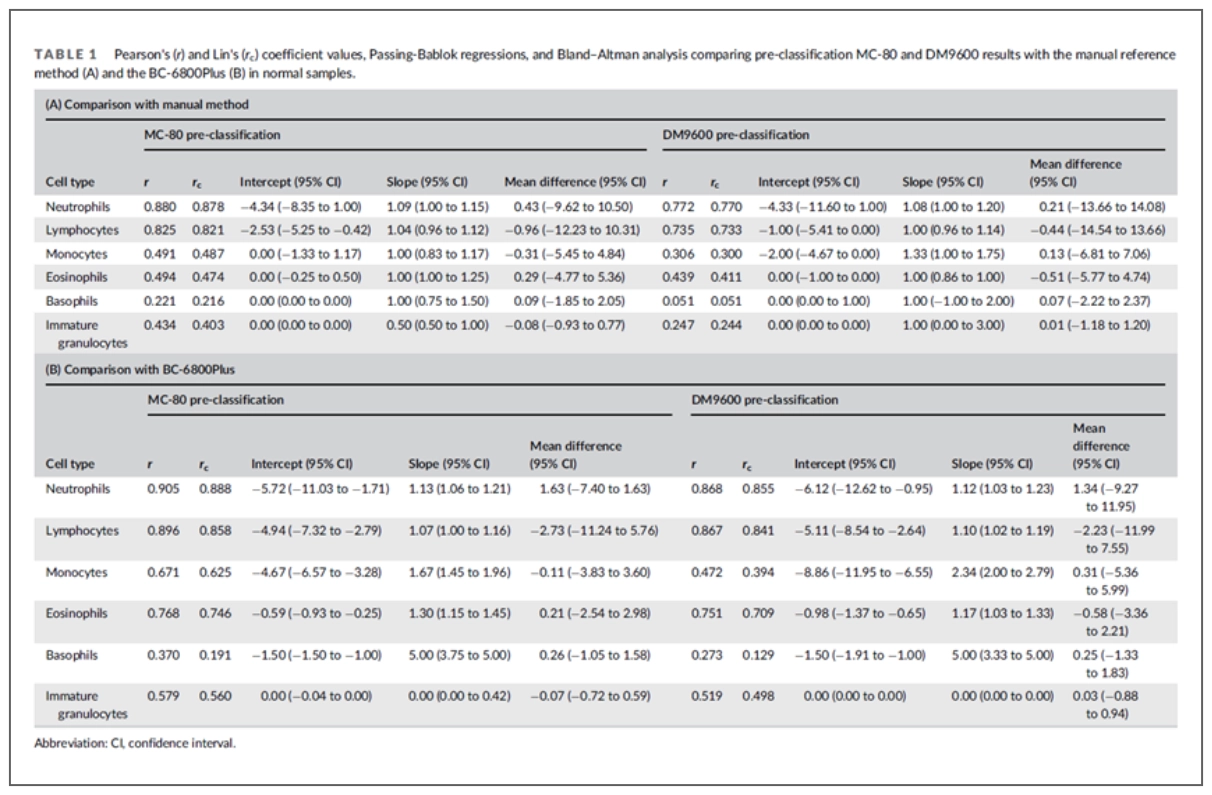
Table 1 shows the pre- and post-classification percentages of WBC obtained using the MC-80, which exhibited a strong correlation and concordance for all types of leucocytes, including immature granulocytes (IG) (values between 0.91 and 1).
\r\n
Table 1 shows the pre- and post-classification percentages of WBC obtained using the MC-80, which exhibited a strong correlation and concordance for all types of leucocytes, including immature granulocytes (IG) (values between 0.91 and 1).
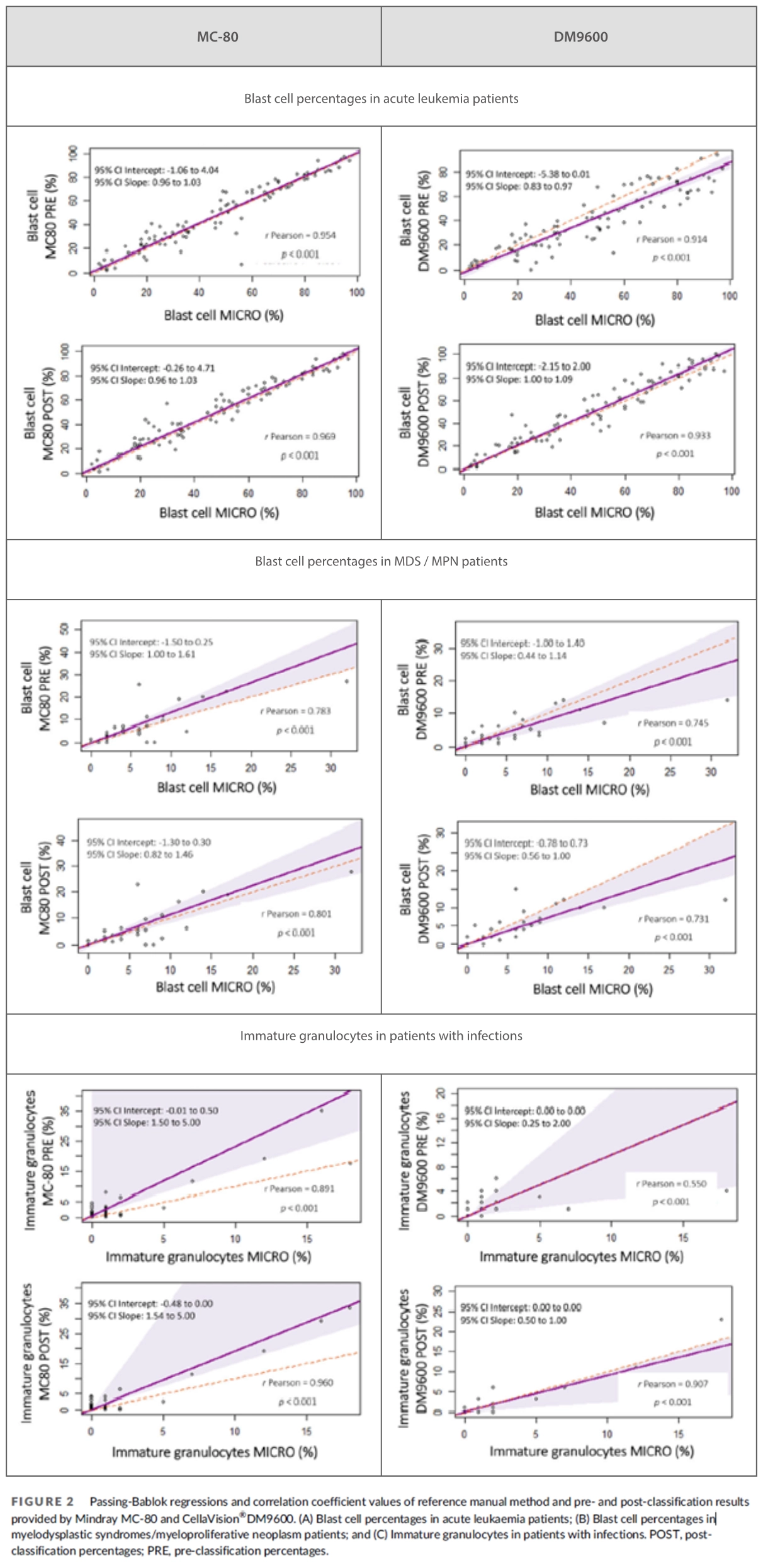
As observed in samples from acute leukemia patients, when comparing pre- and post-classification percentages of blast cells in this group of patients, the MC-80 exhibited the highest correlation and concordance values.
\r\n\r\n
In samples from patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) /myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN), percentages of blast cells using the microscope were similar to pre- and post-classification values provided by the MC-80 and the DM9600.
\r\n\r\n
The pre- and post-classification percentages of immature granulocytes (IG) provided by MC-80 showed much higher correlation and concordance values in patients with infections, especially in the pre-classification.
\r\n
As observed in samples from acute leukemia patients, when comparing pre- and post-classification percentages of blast cells in this group of patients, the MC-80 exhibited the highest correlation and concordance values.
In samples from patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) /myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN), percentages of blast cells using the microscope were similar to pre- and post-classification values provided by the MC-80 and the DM9600.
The pre- and post-classification percentages of immature granulocytes (IG) provided by MC-80 showed much higher correlation and concordance values in patients with infections, especially in the pre-classification.
“We found that the MC-80 shows high performance for WBC differentials for both normal samples and patients with hematological diseases.”
\r\n
“We found that the MC-80 shows high performance for WBC differentials for both normal samples and patients with hematological diseases.”
Bangkok, Thailand
\r\nNine hundred and thirty-four samples (100 normal and 834 blood samples triggered a flag on the hematology analyzers) were randomly collected. [4]
\r\n"}}" id="text-3b506b382f" class="8f00b2 cmp-text">Bangkok, Thailand
Nine hundred and thirty-four samples (100 normal and 834 blood samples triggered a flag on the hematology analyzers) were randomly collected. [4]
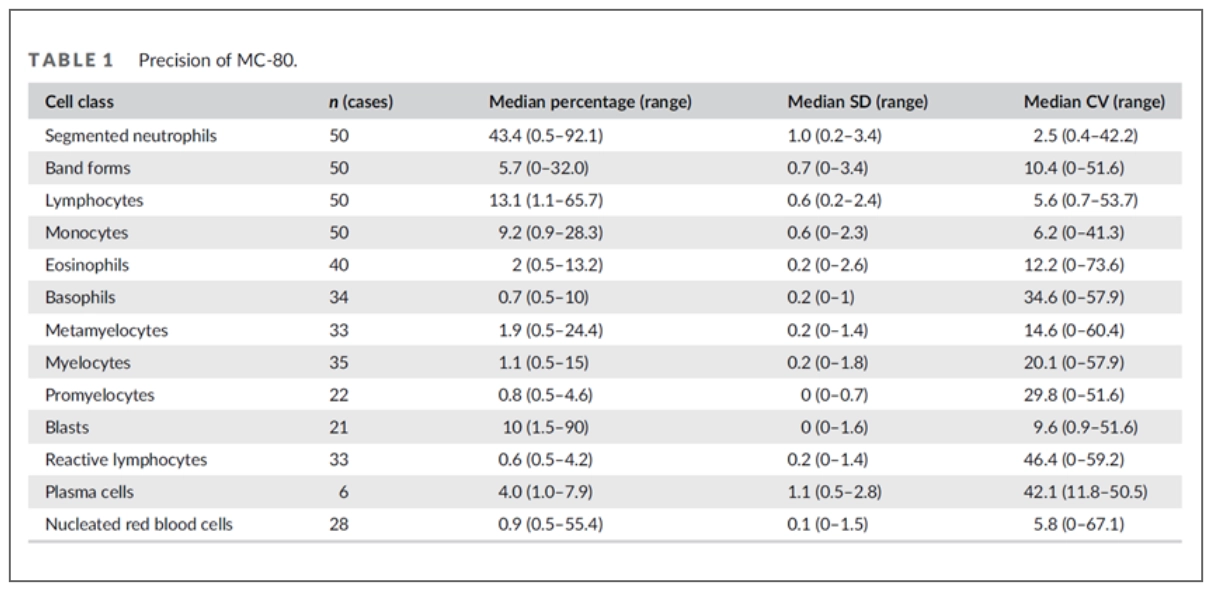
The WBC counts of 24 selected samples ranged from 2.74 x 109 /L to 62.33 x 109 /L. All cell types showed acceptable precision.
\r\n
The WBC counts of 24 selected samples ranged from 2.74 x 109 /L to 62.33 x 109 /L. All cell types showed acceptable precision.
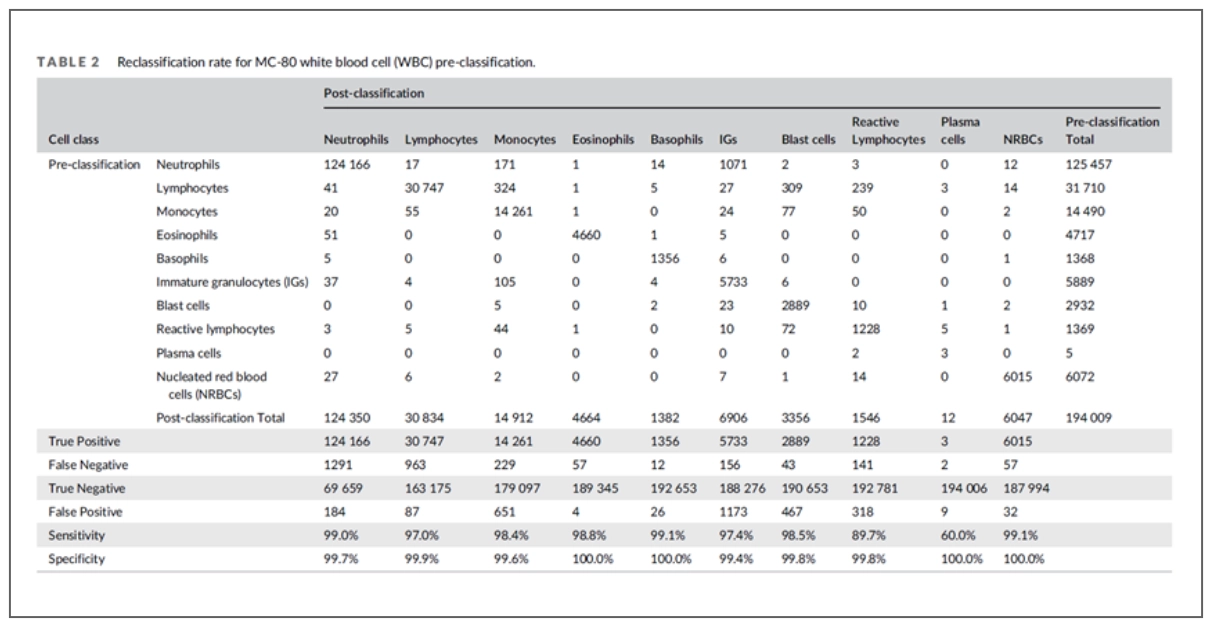
The cell identification performance was analyzed on 194,009 cells from 934 blood smears. Overall, the specificity of cell identification was higher than 95% for all cell classes, and sensitivity greater than 95% for most cell classes. The lowest sensitivity was found in plasma cells. It should be noted that the total number of analyzed plasma cells was considerably low (n = 5).
\r\n"}}" id="text-2bb74903df" class="8f00b2 cmp-text">The cell identification performance was analyzed on 194,009 cells from 934 blood smears. Overall, the specificity of cell identification was higher than 95% for all cell classes, and sensitivity greater than 95% for most cell classes. The lowest sensitivity was found in plasma cells. It should be noted that the total number of analyzed plasma cells was considerably low (n = 5).
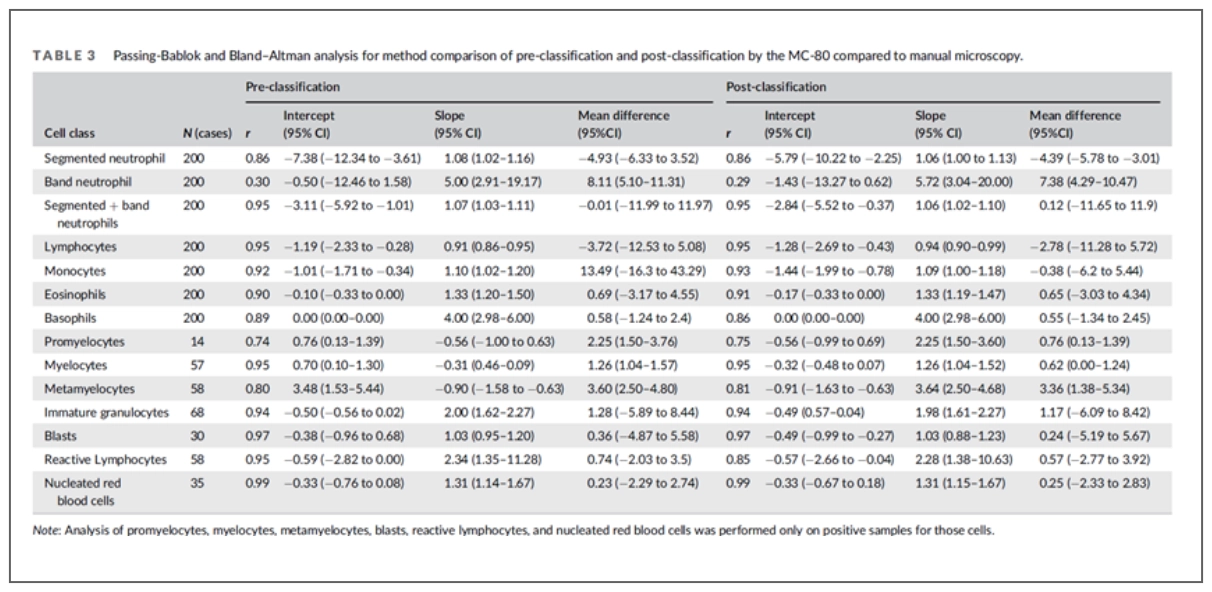
Compared to manual counting, MC-80 yields a good correlation (r > 0.90) and minimal differences for most cell classes. The highest correlation was found in nucleated red blood cells (NRBC) (r = 0.99).
\r\n
Compared to manual counting, MC-80 yields a good correlation (r > 0.90) and minimal differences for most cell classes. The highest correlation was found in nucleated red blood cells (NRBC) (r = 0.99).
In conclusion, the performance of the WBC differential of the newly released Mindray MC-80 automated digital cell morphology analyzer is acceptable compared to the manual differential.
\r\n
In conclusion, the performance of the WBC differential of the newly released Mindray MC-80 automated digital cell morphology analyzer is acceptable compared to the manual differential.

The number 3 holds great inspiration. 3 esteemed morphologists, through their remarkable work on MC-80's 3-year evaluation, have instilled incredible confidence in the analyzer. This has established MC-80 as a trusted tool for serving laboratories worldwide.
[2]Zini G, Mancini F, Rossi E, Landucci S, d'Onofrio G. Artificial intelligence and the blood film: Performance of the MC-80 digital morphology analyzer in samples with neoplastic and reactive cell types. Int J Lab Hematol. 2023 Dec;45(6):881-889. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.14160. Epub 2023 Aug 28. PMID: 37641457.
\r\n[3]Merino A, Laguna J, Rodríguez-García M, Julian J, Casanova A, Molina A. Performance of the new MC-80 automated digital cell morphology analyser in detection of normal and abnormal blood cells: Comparison with the CellaVision DM9600. Int J Lab Hematol. 2023 Sep 25. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.14178. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37746889.
\r\n[4]Khongjaroensakun N, Chaothai N, Chamchomdao L, Suriyachand K, Paisooksantivatana K. White blood cell differentials performance of a new automated digital cell morphology analyzer: Mindray MC-80. Int J Lab Hematol. 2023 Oct;45(5):691-699. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.14119. Epub 2023 Jun 20. PMID: 37338111.
\r\n"}}" id="text-24e0f25e44" class="8f00b2 cmp-text">References
[1]http://www.htworld.co.uk/insight/opinion/digital-morphology-what-advances-mean-for-modern-laboratories-and-why-continued-innovation-is-imperative-hm23/
[2]Zini G, Mancini F, Rossi E, Landucci S, d'Onofrio G. Artificial intelligence and the blood film: Performance of the MC-80 digital morphology analyzer in samples with neoplastic and reactive cell types. Int J Lab Hematol. 2023 Dec;45(6):881-889. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.14160. Epub 2023 Aug 28. PMID: 37641457.
[3]Merino A, Laguna J, Rodríguez-García M, Julian J, Casanova A, Molina A. Performance of the new MC-80 automated digital cell morphology analyser in detection of normal and abnormal blood cells: Comparison with the CellaVision DM9600. Int J Lab Hematol. 2023 Sep 25. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.14178. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37746889.
[4]Khongjaroensakun N, Chaothai N, Chamchomdao L, Suriyachand K, Paisooksantivatana K. White blood cell differentials performance of a new automated digital cell morphology analyzer: Mindray MC-80. Int J Lab Hematol. 2023 Oct;45(5):691-699. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.14119. Epub 2023 Jun 20. PMID: 37338111.